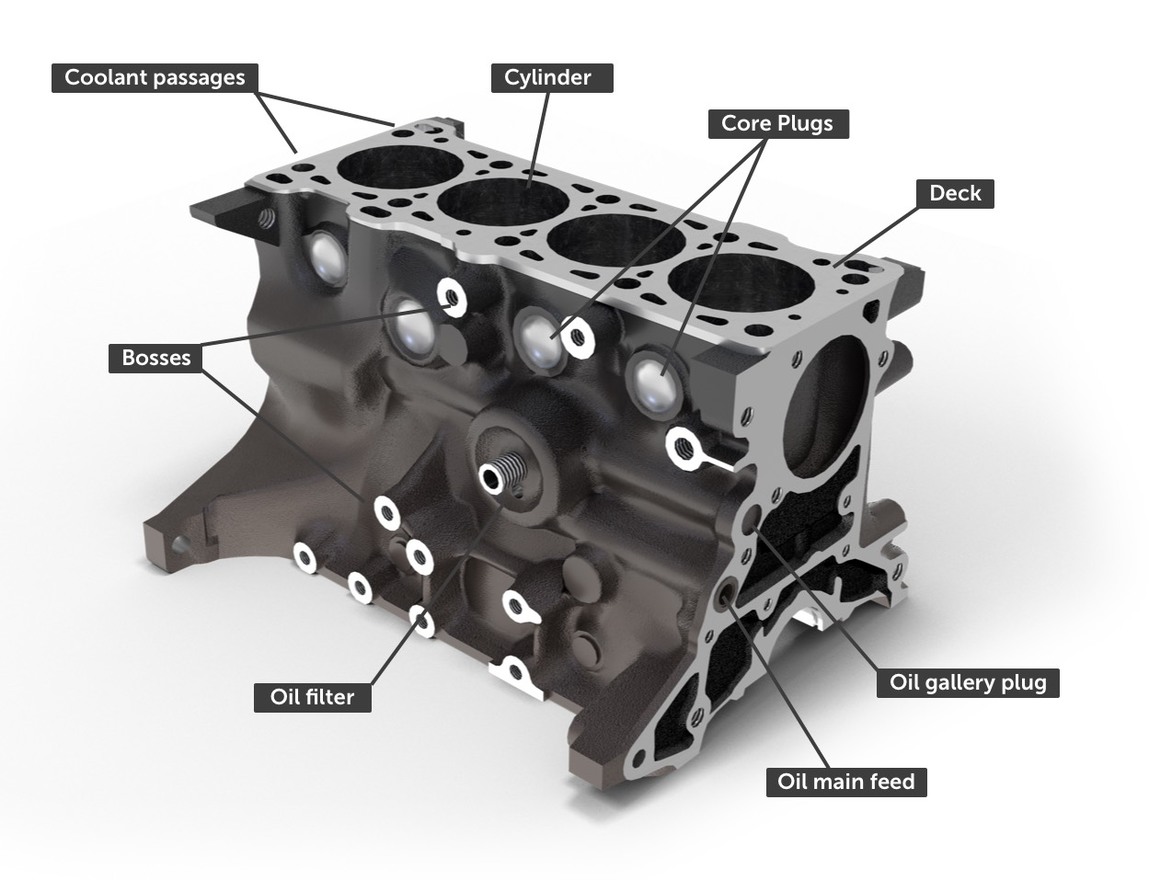
The cylinder block, also known as the engine block, is the main structure of an internal combustion engine.
It contains the cylinders, coolant passages, and other components essential for the combustion process. The cylinder block acts as the central frame of the engine, to which all the other engine components are attached.
It is typically made of cast iron or aluminum alloy, providing strength and the ability to transmit heat from the combustion process. The block also houses the crankcase, water cooling system, and oil galleries for lubrication. In modern engines, the cylinder block is often a single integrated component, known as a monobloc, which reduces production costs.
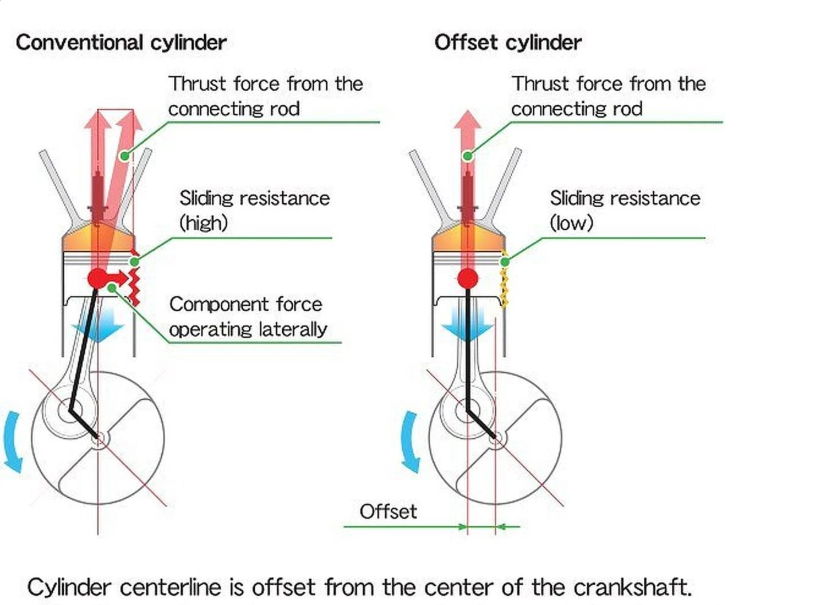
The cylinder block plays a key role in the lubrication, temperature control, and stability of the engine. When the cylinder head is in place, together with the camshaft, the pistons move up and down within the cylinders and turn the crankshaft, which ultimately drives the transmission.
How does the cylinder block affect engine performance?
The cylinder block, also known as the engine block, significantly affects engine performance in several ways.
It houses the cylinders, where the fuel is burned and converted into energy, and provides support for various engine components. The material and design of the cylinder block play a key role in the engine’s temperature control, lubrication, and stability. Additionally, the cylinder block’s ability to withstand high temperatures and loads is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance.
A damaged cylinder block can lead to issues such as oil leaks, low compression, and overheating, which can significantly impact the engine’s efficiency and reliability.